Cracking the Code: Understanding Interest Rates Like a Pro
Interest rates are everywhere — hiding in mortgage agreements, dancing through credit card bills, and quietly shaping the economy. Yet for many people, they remain a mystery wrapped in a percentage. What exactly is an interest rate? Why does it rise and fall? And how does it influence everyday decisions, from buying a home to paying off a loan? It’s time to crack the code.

🧠 What Is an Interest Rate, Really?
At its core, an interest rate is the cost of borrowing money. Think of it as the "rental fee" you pay to use someone else's money for a certain period. If you borrow $1,000 from a bank at a 5% annual interest rate, you’ll owe $1,050 at the end of the year.
But it’s not just about borrowing — interest rates also reward savers. When you deposit money in a savings account, the bank pays you interest for holding your funds. Essentially, you're loaning the bank your money, and they’re paying you rent for it.
📈 The Two Sides of the Coin: Borrowers vs. Savers
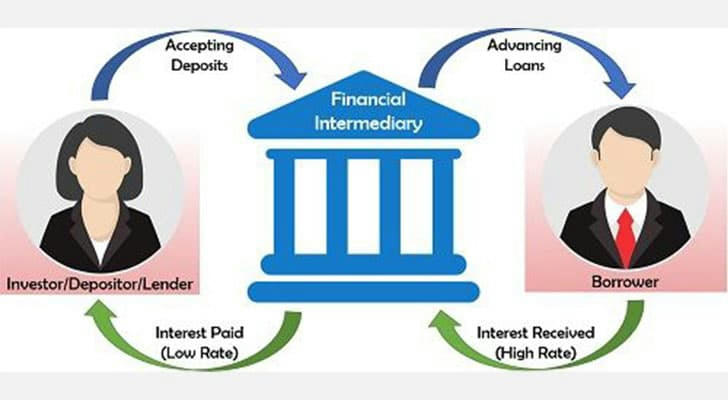
Borrowers love low interest rates. Lower rates make mortgages, student loans, car payments, and business financing more affordable.
Savers cheer for high interest rates. The higher the rate, the more they earn on deposits, certificates of deposit (CDs), and other fixed-income instruments.
It's a delicate balance. One person’s gain is often another person’s pinch.
🕹️ Who Controls Interest Rates?
Contrary to what some may think, interest rates aren't decided by rolling a dice in a secret room. Central banks — like the U.S. Federal Reserve — play a major role. They adjust a key interest rate known as the federal funds rate, which influences short-term interest rates across the economy.
When inflation is rising too quickly, central banks may raise rates to slow down spending. When the economy stalls, they may lower rates to encourage borrowing and investment. It’s monetary policy in action, and it affects nearly everyone, even if they never step into a bank.
🔍 Fixed vs. Variable: Which One Are You Dealing With?
There’s more than one type of interest rate, and knowing the difference can make or break your budget.
Fixed interest rates stay the same over time. Predictable and stable — no surprises.
Variable interest rates fluctuate based on market conditions. Great when rates go down, stressful when they go up.
A mortgage with a fixed rate brings peace of mind, while a credit card with a variable rate might suddenly cost more than expected after a rate hike.
🏦 APR vs. Interest Rate: Don’t Confuse the Two
Many people use these terms interchangeably, but they’re not quite the same.
The interest rate is just the cost of borrowing.
The APR (Annual Percentage Rate) includes the interest rate plus other fees and costs associated with the loan.
So if you're comparing loan offers, look at the APR for a truer picture of what you’ll be paying.
💡 How Interest Rates Affect Your Wallet

Let’s bring it down to earth. Imagine these three common scenarios:
Buying a House
A 1% change in mortgage interest can make a $30,000 difference over a 30-year loan. That’s not pocket change.
Credit Cards
Carrying a balance on a card with a 22% APR? That’s money leaking from your bank account every single day. Paying it down fast can save hundreds.
Savings Accounts
When rates are low, traditional savings might earn less than a cup of coffee per year. Exploring high-yield savings or CDs becomes more attractive.
🧭 How to Navigate Interest Rates Like a Pro
Here are some practical tips:
Read the fine print: Always check whether a rate is fixed or variable.
Shop around: Lenders compete. Don’t accept the first rate you’re offered.
Use interest to your advantage: High rates can boost savings. Low rates can make it the right time to invest in real estate or education.
Pay attention to the Fed: Their decisions today shape the financial opportunities tomorrow.
🧮 Compound Interest: The Eighth Wonder of the World?
Einstein allegedly called it the most powerful force in the universe — and for good reason.
Compound interest means you earn interest on your interest. It’s how savings grow exponentially over time. Whether it’s helping you build wealth or causing debt to snowball, compound interest is no joke.
For example, saving $200 per month at a 6% annual return could turn into over $46,000 in 10 years. Let it ride longer, and the growth becomes even more dramatic.
🎢 Why Interest Rates Fluctuate
Several factors cause interest rates to move:
Inflation expectations
Economic growth
Government debt
Global events
When inflation rises, lenders want higher returns to offset the loss in purchasing power. When recessions loom, central banks step in to soften the blow with lower rates. It's an ongoing balancing act.
📚 A Lifelong Learning Curve
Understanding interest rates isn’t just about passing a finance quiz. It’s a survival skill in today’s economy. Whether you're financing a car, saving for retirement, or running a business, interest rates are your silent financial partner.
They don’t always shout, but they’re always there — in your statements, in your payments, and in the fine print. Learning how they work puts the power back in your hands.
Final thought: Interest rates might seem complex, but they're more approachable than they appear. Behind the math is a story of economics, psychology, and real-world impact. And once you know how to read that story, you’re no longer guessing — you’re strategizing.
Welcome to the ranks of interest rate insiders. 📊
